
Shannon showed that adding extra bits to a signal allowed transmission errors to be corrected. In this paper, he focused on the conditions under which information encoded by a transmitter and transmitted through a noisy communication channel can be restored to its destination, i.e. The Fundamental Unit of InformationĪfter a short stay as a researcher at the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, he joined AT&T Bell Labs in 1941 as a mathematician. In 1948 Claude Shannon published his groundbreaking work A Mathematical Theory of Communication, which introduced the word “bit” as the fundamental unit of information for the first time. In 1940 he received his doctorate in mathematics with a thesis on theoretical genetics ( An Algebra for Theoretical Genetics) at MIT. The work arose from the analysis of the relay circuits in Vannevar Bush‘s Differential Analyzer analog computer, which Shannon programmed for users. In his master thesis (1937), A Symbolic Analysis of Relay and Switching Circuits, he applied Boolean algebra to construct digital circuits. In 1936 he moved to MIT with a degree in mathematics and electrical engineering.

During his high school years he worked as a messenger for the Western Union. He followed his sister Catherine to the University of Michigan in 1932. His father was a judge, his mother a language teacher of German origin. Claude Shannon, Youth and EducationĬlaude Shannon was born in a hospital in Petoskey, Michigan, and grew up in nearby Gaylord, the home of his parents.

Thus we may have knowledge of the past but cannot control it we may control the future but have no knowledge of it.” “This duality can be pursued further and is related to a duality between past and future and the notions of control and knowledge. Shannon contributed to the field of cryptanalysis during World War II and afterwards, including basic work on code breaking. Believe it or not, it has been claimed that this was the most important master’s thesis of all time. But he is also credited with founding both digital computer and digital circuit design theory in 1937, when, as a 21-year-old master’s student at MIT, he wrote a thesis demonstrating that electrical application of Boolean algebra could construct and resolve any logical, numerical relationship.
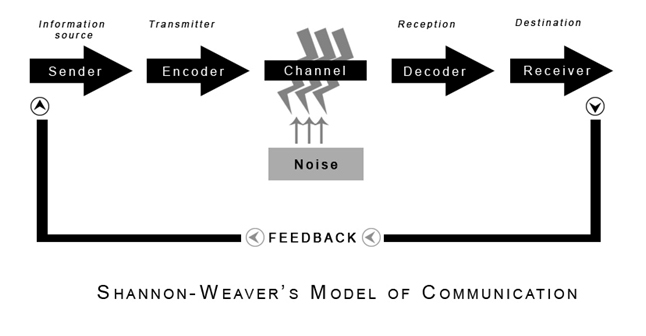
Of course Shannon is famous for having founded information theory with one landmark paper published in 1948. On April 30, 1916, American mathematician, electrical engineer, and cryptographer Claude Elwood Shannon was born, the “father of information theory“, whose groundbreaking work ushered in the Digital Revolution. Shannon (1916-2001), photo: Jacobs, Konrad, CC BY-SA 2.0 DE, via Wikimedia Commons


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
